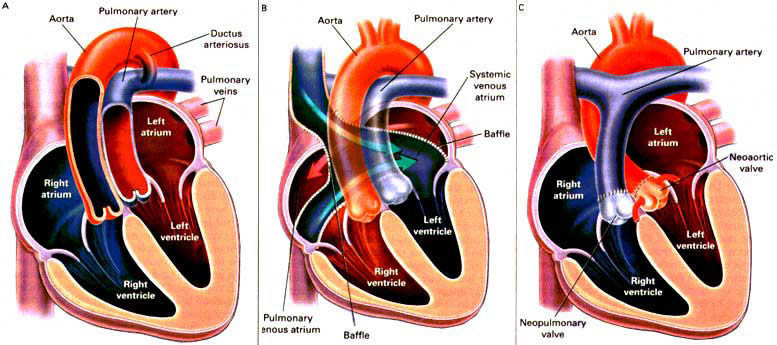
Figure 23i
Transposition and Switching of the
Great Arteries.
In D-transposition of the great arteries (complete transposition)(Panel
A), systemic venous blood returns to the right atrium, from which it
goes to the right ventricle and then to the aorta. Pulmonary venous
blood returns to the left atrium, from which it goes to the left ventricle
and then to the pulmonary artery. Survival is possible only if there
is a communication between the two circuits, such as a patent ductus
arteriosus. With the "atrial switch" operation(PanelB), a pericardial
baffle is created in the atria, so that blood returnig from the systemic
venous circulation is directed into the left ventricle and then the
pulmonary artery (blue arrow), whereas blood returning from the pulmonary
venous circulation is directed into the right ventricle and then the
aorta (red arrow). With the "arterial switch" operation (Panel C), the
pulmonary artery and the ascending aorta are transected above the semilunar
valves and the coronary arteries, then switched (neoaortic and neopulmonary
valves).