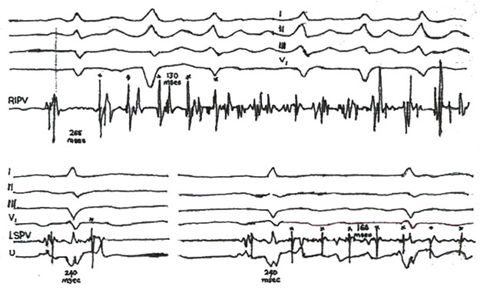
Figure 11h
Two
Examples of the Onset of Atrial Fibrillation from Foci in a Right Inferior
Pulmonary Vein and a Left Superior Vein.
The electrogram with the pulmonary vein spike is the terminal part of
a two-component electrogram obtained during sinus rhythm. In the upper
panel, a burst of five spikes (astericks) with a mean cycle length of
170msec induced continuous electrical activity in the right inferior
pulmonary vein (RIPV), with coarse atrial fibrillation on the surface
electrocardiogram. The coupling interval of the first spike was 265msec.
In the bottom panel on the left,a sinus beat (with a terminal spike)
was followed by an isolated atrial ectopic beat(asterick) at a coupling
of 240msec. The electrogram of the ectopic beat characteristically shows
temporal reversal, with the rapid deflection spike preceding the lower
amplitude, slower far-field atrial activity. On the right, in the same
patient, a train of spike discharges (astericks) at a cycle length of
160msec sets off atrial fibrillation. The spike discharges are also
characterized by temporal reversal but exhibit a progressively prolonged
conduction time to the atria. The coupling interval of the first spike
on the right (240msec) is identical to that of the isolated ectopic
beat on the left. LSPV denotes left superior pulmonary vein, and U unipolar
left atrial activity.
.Reference:Haaissaguerre,M.,and others,Spontaneous Initiation of Atrial Fibrillation by Ectopic Beats Originating In The Pulmonary Veins,N.Engl.J.Med.1998:339;659-66