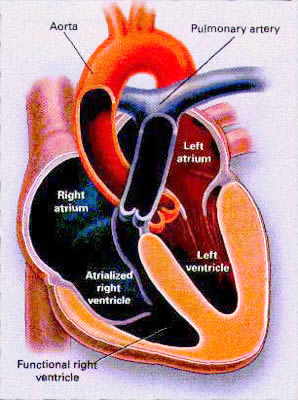
Figure 23e
In D-transposition of the great arteries (complete transposition), systemic venous blood returns to the right atrium, from which it goes to the right ventricle and then to the arota. Pulmonary venous blood returns to the left atrium, from which it goes to the left ventricle and then to the pulmonary artery. Survival is possible only if there is a communication between the two circuits, such as a patent ductus arteriosus.
Brickner, M.E., Hillis, L.D., and Lange, R.A., Medical Progress: Congenital Heart Disease in Adults (first of two parts), The New England Journal of Medicine, p 334-343.